Data Structure: Interview Experience Part 6(Microsoft)
Data Structure: Interview Experience Part 6(Microsoft)
LinkLists
1. Reverse a singly linked list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
Follow up:
A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you implement both?
Practise: https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
Iterative Solution:
Recursive Solution:
2. Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer
pos which
represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where
tail connects to. If
pos is
-1, then there
is no cycle in the linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.

Practise: https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
3.
Add Two Numbers
You are given two
non-empty
linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits
are stored in
reverse order
and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two
numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example:
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Practise: https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
4.
Add Two Numbers II
You are given two
non-empty
linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most
significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contain a
single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked
list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Follow up:
What if you cannot modify the input lists? In other
words, reversing the lists is not allowed.
Example:
Input: (7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
Practise: https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers-ii/
5.
Merge Two Sorted Lists
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new
sorted
list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes
of the first two lists.
Example:
Input: 1->2->4, 1->3->4
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4
Practise: https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
6. Merge k Sorted Lists
Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexity.
Example:
Input:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
Practise: https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity : O(Nlogk) where k is the number of linked lists.
- We can merge two sorted linked list in O(n) time where n is the total number of nodes in two lists. Sum up the merge process and we can get: O(∑i=1log2kN)=O(Nlogk)
- Space complexity : O(1)
7. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:

begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
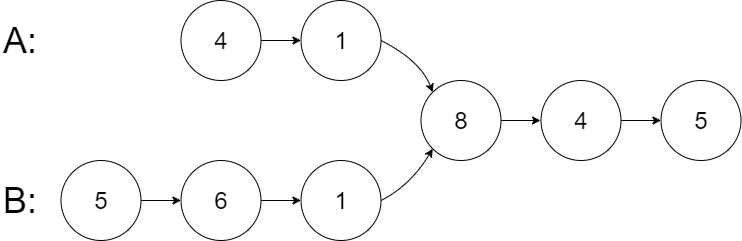
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Practise: https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
8. Copy List with Random Pointer
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
The Linked List is represented in the input/output as a list of
n nodes. Each
node is represented as a pair of
[val, random_index]
where:
-
val: an integer representingNode.val -
random_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) where random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Example 1:
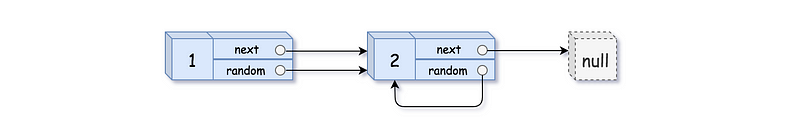
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Practise: https://leetcode.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
Hope this article is useful for people looking to learn and practice Data structure & Algorithm in swift, Please ❤️ to recommend this post to others 😊. Let me know your feedback. :)